We help the world growing since 2023
Many different industries use automatic orbital gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) to help their products achieve maximum leak integrity, high performance, and ultra-cleanliness. The process is used in various applications, from the biopharmaceutical and semiconductor industries to petrochemical and power plants to chemical processing and refining operations.
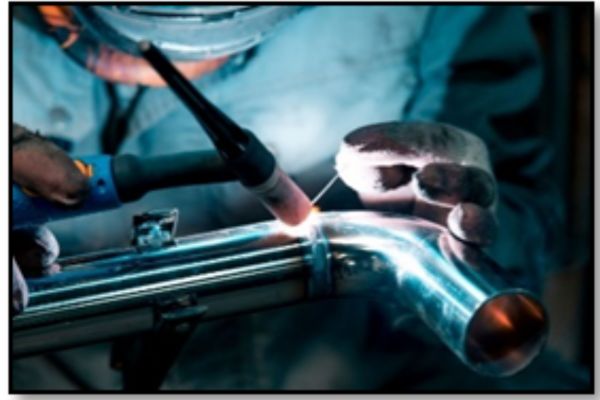

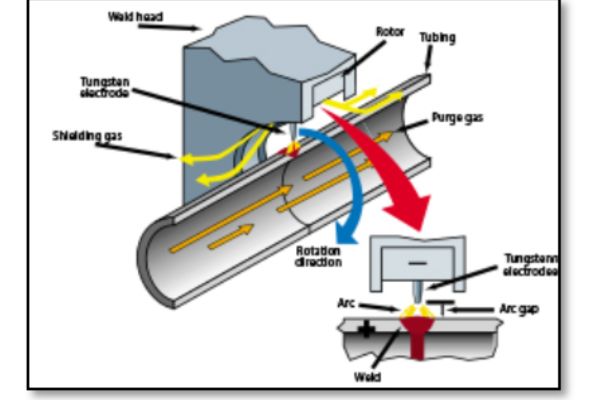
Automatic orbital GTAW establishes an arc between a non-consum¬able tungsten electrode (positioned in the weld head) and the base material that is being welded, creating a weld puddle. The electrode and weld puddle both are surrounded by a shielding gas, which is fed through the weld head to protect the electrode, molten weld puddle, and solidifying weld metal from atmospheric contamina¬tion. The heat produced by the arc melts the base material, and the electrode moves along the joint and progressively melts and joins the adjoining surfaces
Small, portable inverter power supplies, advanced control systems, and other developments have made orbital GTAW systems practical for many applications The advent of new technology has led to further im¬provements in the systems’ ease of use, weld consistency, and weld reliability. Open Platform Design
Orbital welding power supplies have been incorporating more skills of the welder into the welding system itself, enabling efficiencies in automation, programming, and documentation. An open platform design allows an interface with standard devices and the ability to expand as technology evolves and needs change.

Aspects of the welding process that historically would be undertaken manually, such as travel speed, arc gap, cur¬rent control, and gas flow, are controlled through electronic and mechanical means. This minimizes many of the variables in the welding process that can lead to errors or defects and enables welders to focus on overseeing the process and completing actual welds.
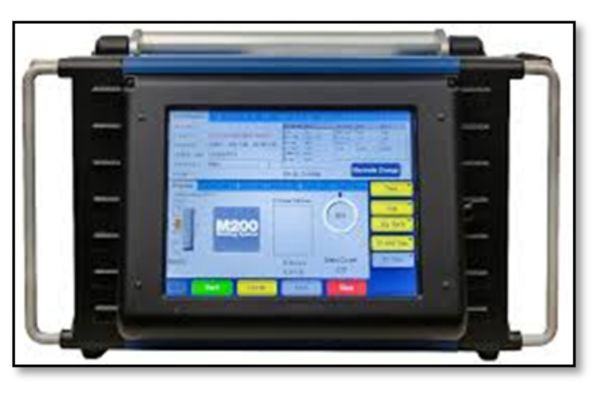

Every orbital weld, regardless of the application, requires the creation of a program that controls the output characteristics of the system. Systems can simplify programming by providing step-by-step procedures to create programs for many different tube diameters, wall thicknesses, and base materials. Rather than build programs manually using charts or tables, past weld parameter data, or memory, operators can create programs by selecting pertinent data from pick lists or drop-down menus. The system then creates the initial program for the operation, which reduces the chance for human error and decreases start-up time. This feature also is helpful for operators welding unfamiliar materials. Newer orbital welding systems are available with integral USB ports that enable operators to plug in a keyboard, mouse, or number keypad for simplified data entry. Operators also can download welding programs via a USB flash drive or update operating system software to add features or functionality.
Newer orbital power supply designs feature automatic shield gas control to the weld head. This helps eliminate operator inefficiency or the possibility of incorrect settings that could negatively affect weld quality. The controller adjusts gas flow automatically based on the program selected for a particular weld. The integrated flow controller also prevents operators from initiating the weld without gas flow, an error that could result in damage to the weld head or the workpiece.
In some industries, documentation of the weld is important for qual¬ity assurance and control. Traditionally, weld operators have had to maintain detailed, written weld logs that must be entered into data¬bases and formatted into reports. Today’s orbital welding technolo¬gy enables this data to be stored within the system for retrieval and transfer to databases for analysis and reporting. Data management can help an organization track trends, review production rates, and calculate costs per weld. High-speed thermal printers built into newer orbital welders also help with documentation
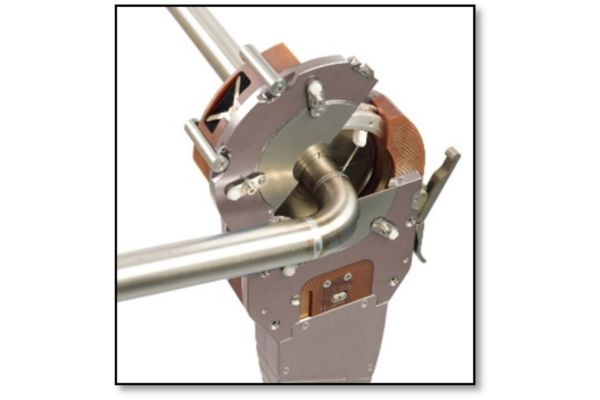
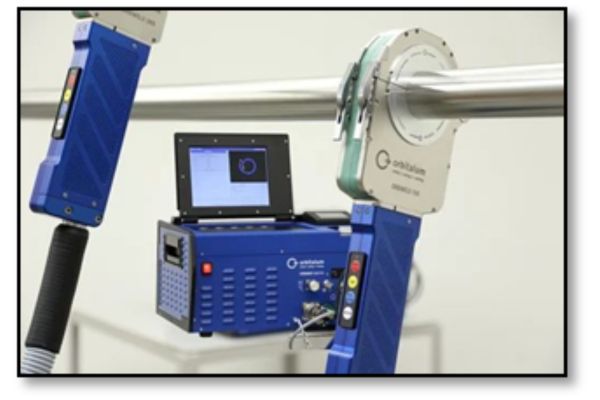


With orbital welding, the electrode is rotated in an orbit around a joint on a rotor. The rotor and electrode are housed in the weld head, which rotates around the tube. The process is highly controlled to help ensure that high-quality welds can be produced on a consistent and repeatable basis. Variables are maintained at preset levels. The system automatically starts and completes the weld, stepping from one variable setting to the next at specific loca tions along the joint or at predetermined times during the process.
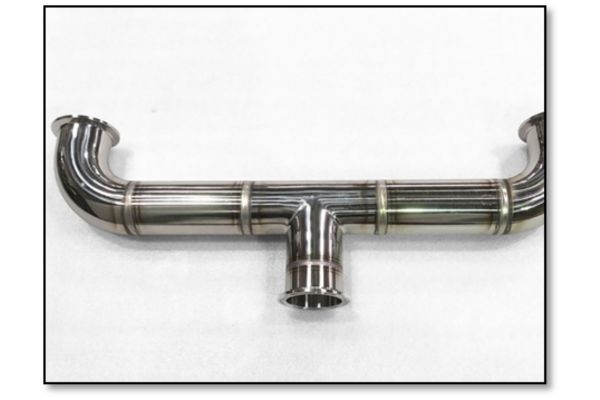


Power supplies with high power outputs can weld larger-diameter and heavy-walled tube and pipe while main¬taining consistent welds. Newer welding systems offer the power output needed to weld the heavy-walled com¬ponents found in general industrial applications like oil and gas, as well as smaller-diameter, thin-walled tubing for R&D or semiconductor applications. Initializing the welding process requires a high-frequency, high-voltage arc start, which could result in electromagnetic interference (EMI). EMI is an electrical disturbance that can interfere with devices such as computers and other sensitive electronics. Excessive EMI in a welding project could cause computers to shut down and work to be lost. Welding systems with low-EMI arc start technology allow the arc start to occur without affecting the operation of equipment in proximity.
.We are ready for SEMICON industry, the purity is very important role playing in SEMICON field. Orbital welding performs very clean welding at internal side as well as external.
Most semiconductor welding is done using weld Heads which fully enclose the joint, ensuring superior gas coverage and minimized any oxidation of the weld bead. Wall thickness and tube material generally allows fusion welding to be done in a single pass, without added filler wire.
Orbital welding plays a critical role in the semiconductor industry, where the purity of components is vital. As mentioned above, one of the key benefits of orbital welding in semiconductor manufacturing is its ability to produce high-purity welds. This is accomplished by controlling the atmosphere around the weld, ensuring that the weld area is free from contaminants. In addition, orbital produces a smooth and even weld, which helps to eliminate the crevices and pits that can harbor contaminants and lead to corrosion.
Orbital is also ideal for creating components that require precision and consistency. For example, when welding tubes and pipes, the machine is programmed to follow a specific path and maintain the exact welding parameters, resulting in consistent and repeatable welds. This level of precision is essential in the semiconductor industry, where even the smallest deviation from the desired specifications can result in significant quality issues.
There are a few key factors to consider when selecting an orbital welding system, including:
important considerations when choosing an orbital welding system is its ability to meet the specific welding parameters required for the job. These parameters can include variables such as the diameter of the tubing or pipe, the wall thickness of the material, and the type of material being welded.
Another important consideration is the compatibility of the welding head with the workpiece. The welding head must be able to securely grip the workpiece and maintain a consistent welding distance throughout the welding Process.
The ease of use of the orbital welding system is also an important consideration, as it can impact the efficiency of the welding process. Look for systems with intuitive controls and software that is easy to navigate.
Finally, reliability is crucial when selecting an orbital welding system. You'll want a system that is built to last and can withstand the demands of a high-volume manufacturing environment.
Maintaining the semiconductor fabrication process requires a range of cooling tubes and equipment. This equipment ensures that the processing can be accomplished in the defined temperature range. To ensure the high-quality fusion of these tubes and pipes, orbital welding offers the ideal solution, with advantages like speed, precision, and repeatability that add value to the semiconductor manufacturing process.
The orbital semiconductor welding process offers: